•
11-minute read



Several SEO topics traditionally stir up a lot of talks and controversy. Keyword or content cannibalization is one of them. Different opinions exist: some voices are saying it's an issue, whereas the others are not sure about its existence.
So, what is keyword cannibalization? Does it really affect the website's ranking? Let's take a closer look at the phenomenon and find out when it is an issue and when not. In case it is, we'll need to know how to detect and fix it.
In general, keyword cannibalization is a phenomenon seen when several site pages appear in a SERP for the same keyword. It may occur when different pages are optimized for the same keyword or if Google believes them to be relevant to that keyword. And there's a wide-spread belief that the competing pages hurt each other's ranks.
However, there is a common misconception about keyword cannibalization. It is to believe that when it occurs, it will necessarily end up lowering pages' ranks. The belief is rooted in the idea that search engine bots get confused with what page to choose and may show the wrong page for a certain keyword, which isn't quite right.
Today, search engines can at large define what a page is about. But your and a search engine's idea about what page would be the most relevant for a given search term may differ greatly. Thus, if a search engine believes several pages of the same website are relevant to a query, it will show those pages in SERP. But would those pages cannibalize each other? In short, it depends.
There's no surprise that a certain page may rank for many keywords. According to a study by Ahrefs back in 2017, an average page that takes the first position in a SERP for a popular keyword also ranks in the top-10 for about 1000 other relevant keywords. So intersections inevitably occur.
Following the wide-spread theory, the intersecting pages couldn't take place at the top of a SERP. However, if we check the SERPs, we may find many examples of multiple pages from one site very well positioned for the same (and quite competitive) keywords.
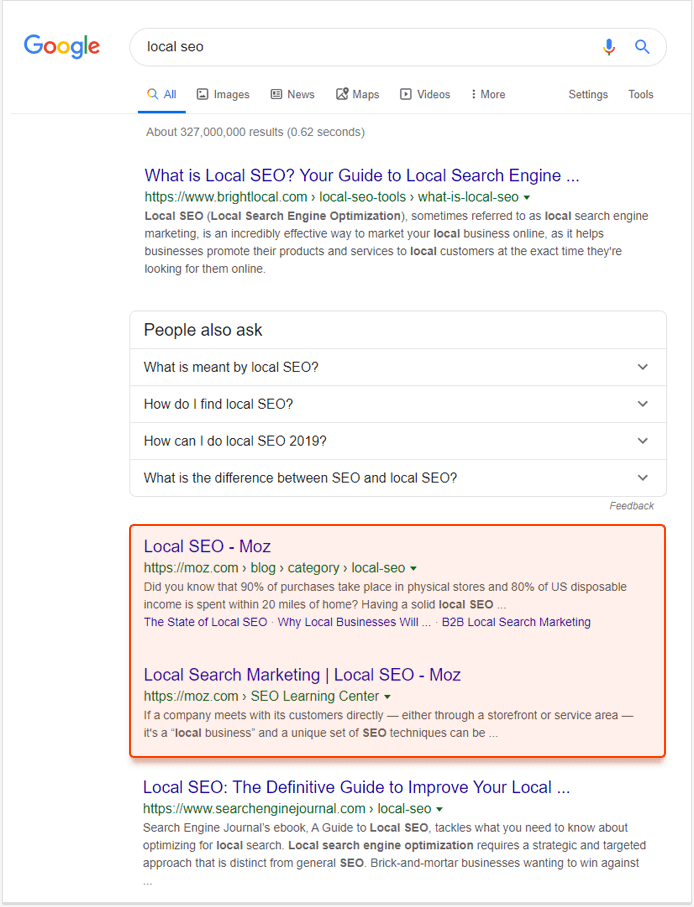
As you can see, the pages are ranked second and third on the first SERP. And if we look at the pages, they are quite similar in type. Both of them are informational resources containing the archives of materials about local SEO. But they cover the topic a bit differently. The first page is a learning hub that introduces the topic to users. The second one is a blog category page that comprises articles describing peculiar tips and aspects of local SEO. Google considers both of them highly relevant and bringing value to users. Otherwise, they wouldn't rank that well.
So, it appears that you may have several pages occupying the top positions of a SERP. And this would not harm your website. Instead, you are likely to boost your visibility, attract more traffic to your website, and improve CTR. This may happen, provided that those pages:
If it's your case, congrats, you may stop worrying about keyword cannibalization.
Now, let's look at the cases of keyword cannibalization that turns out to be a problem and may ruin SEO efforts. And yes, in such cases your ranks may suffer, as well as conversions, CTR, and other important site metrics.
There are several causes of keyword cannibalization, these include:
All these make your pages compete with each other. As a result, your pages get lower ranks or even flip-flop between each other for the same keyword. The latter means that one day one page ranks for a query, the other day another page appears in search for the same query.
Let's take a closer look at the negative aspects of keyword cannibalization.
Diffusion of traffic and conversions loss. As your landing page rivals with another page in a SERP, it may receive less traffic and consequently, fewer conversions.
Loss of content value and website reputation. Having multiple pages that dwell on the same topic (and sometimes not cover it to the full extent) may result in lowering users' trust in the website's expertise and authority.
Bad user experience. Users that do not find what they intended to find on a page are more likely to bounce back than stay and surf the website. And this negatively affects such behavioral factors as bounce rate and dwell time.
Loss of pages' weight. When several pages are optimized for the same keyword — intentionally or not — each may receive less weight from links. The weight gets split between multiple pages instead of being consolidated into one.
These negative effects may bring your SEO efforts to nothing and lead to the loss of time and resources. The solutions are to find and fix cannibalization issues, as well as prevent their occurrence.
The problem with keyword cannibalization is that you don't see it immediately. You may suspect that something goes wrong when your efforts have no or little results. For example, your page doesn't climb to higher positions, despite the optimization steps you take.
The phenomenon may usually occur at different website levels. At metadata level, when multiple pages share the same or very similar meta title and description. And at the content level, when two or more pages appear to be covering the same topic.
To discover these occurrences, you'll need to carefully check your ranks and find out the cases of multiple pages ranking for the same queries. You'll also need to scan your website's metadata, such as titles, descriptions, and canonical tags.
This seems to be a time-consuming task (and it is). Hopefully, today, we have plenty of tools that allow for scraping through it faster. I'll show how to do this, using the SEO PowerSuite tools.
Titles still remain an important ranking signal. They give search engines and users a better idea of what a page is about. Descriptions are often used to create search result snippets. Moreover, good titles and descriptions increase pages' CTR.
So let's start with the easiest part and scan a website for similar meta titles and descriptions.
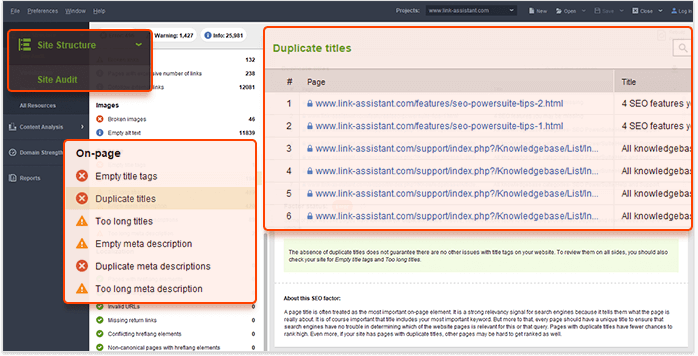
Now, when you have all the pages with duplicate titles and descriptions, you may define which of them you want to target for a certain keyword. For all the others, you need to create unique metatags, more relevant to the pages' content.
You may have assigned certain keywords to certain landing pages. But Google may have its own opinion on what pages to consider relevant for this keyword. So it may rank other pages in addition to your landing page. Sometimes, it ranks them better than your landing page. Rank Tracker may help discover such pages.
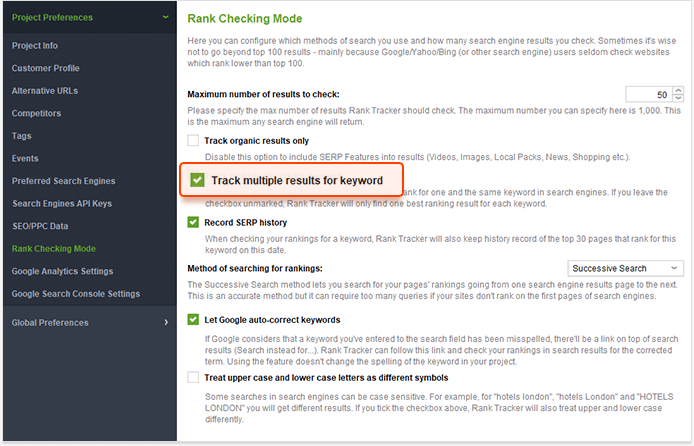
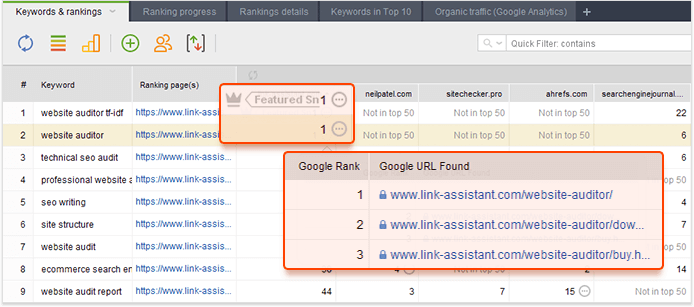
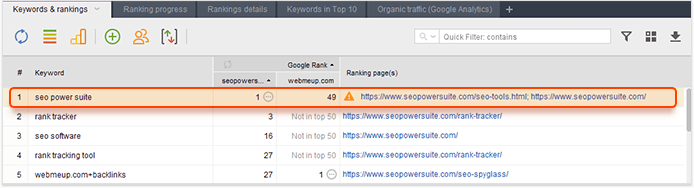
Depending on the results, you'll need to review your pages and make a decision. There may be several ways of fixing content cannibalization. Choose any that suits your case or combine different methods.
This method will suit if you have several pages on the same subject. Analyze the content to select interesting details on each page. Then rewrite the landing, consolidating useful content from different pages into a single more in-depth piece.
Don't forget to eliminate the unneeded pages or set up proper redirects to the new landing.
Make your landing page more relevant to the target keyword. To do this, you'll need to analyze the page with TF-IDF. It's a great solution, and Google uses a similar formula to evaluate the relevance of documents.
TF-IDF analysis allows assessing your piece of content against your top-performing competitors. It gives you a clue on how your competitors use the keyword on their pages. You may also discover additional relevant keywords to introduce into your piece, and thus, increase its relevance. Read this TF-IDF optimization guide for more details.
Internal linking is an extremely important part of SEO. It builds a website structure, as well as helps search engines better understand the importance of site pages. The more pages link to a certain page, the more important it looks in search engines' eyes. Analyze your structure and ensure you have enough links pointing at your landing page through relevant keyword-based anchors.
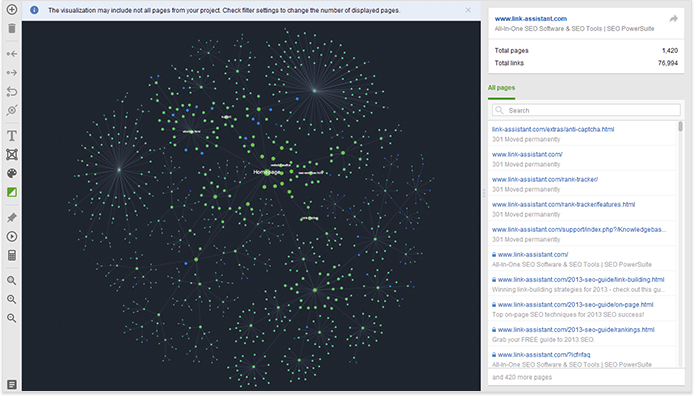
A great way to see the whole picture is to visualize your site structure. There's a variety of tools that allow for this kind of analysis, including WebSite Auditor. It shows your pages' hierarchy on a convenient visual model so that you can see how your pages link to each other, find all the redirects and orphan pages. This website structure visualization guide will give you plenty of useful ideas on how to build an SEO-friendly site structure.
There's another way to show search engines which page out of several similar ones to prioritize. I'm talking about the rel="canonical" tag. The tag is usually placed in the <Head> section of a page and looks like this:
Canonicalisation helps prevent the issue of duplicate content, as well as fights cannibalization. Moreover, it consolidates link signals for similar pages into a single URL. Thus, make sure to use the right canonicals to show search engines which pages you want to appear in the search results. You can find more about defining canonical pages here.
Keyword cannibalization is the disease that is easier to prevent than cure. So either you are just starting to build a website or thinking about creating a new page, you need to provide for cannibalization occurrence at the very beginning. Below are some ways that may help prevent cannibalization issues.
Today, when forming a search results page for a certain keyword, Google takes into account the intent behind this keyword. You should know that there are four major intents: navigational, informational, transactional, and commercial investigation. The search engine analyzes what type of queries people use and what type of result they click to recognize them.
So when you search for target keywords for a new landing page, think about what intent a chosen keyword bears. And creating new content, ensure to cover this intent. Thus, the landing page will more likely be recognized as the most relevant for this keyword out of your other pages dwelling on a similar topic.
This point is closely connected with the previous one. Before creating a piece of content for a landing page, analyze the results, search engines show for the target keywords. This step will save you lots of time and effort in the future.
Look what types of pages are shown at large for a given keyword. What intent do they cover? Obviously, it would be hard to rank well for an informational search query if your content covers transactional intent, etc.
Keyword mapping is an often underrated but great solution. Together with a content strategy, it may help you prevent keyword cannibalization and understand what content you'll need to create in the future.
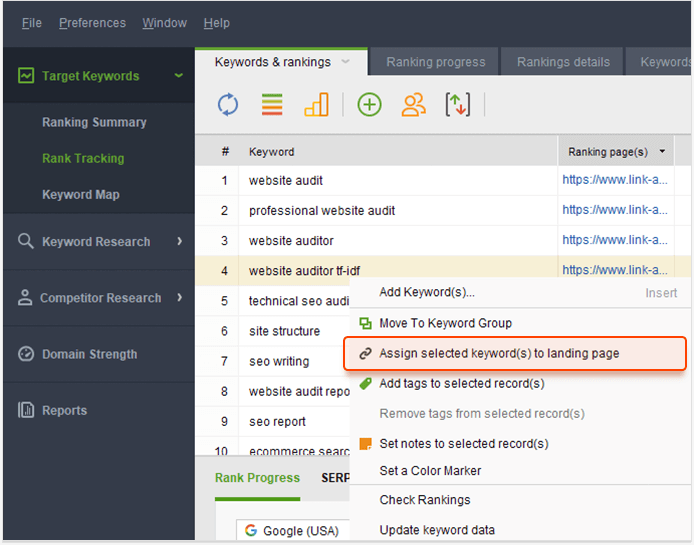
You may use a keyword mapping spreadsheet that may contain, for example, your existing pages with keywords assigned to them, combined with a content plan. You may also use a keyword mapping tool, for example, the one built into Rank Tracker.
It is easy to use and allows for mapping certain keywords or groups of keywords to landing pages.
Though keyword cannibalization more often affects big websites that have a huge amount of pages, it may cause trouble for smaller sites as well. The major problem with it is that it's hard to predict and detect until you face its consequences. Regular website audits and position tracking, however, may help find it faster. Moreover, SERPs analysis, proper keyword mapping, and an intent-based approach may help prevent it when you create new content. And remember, high-quality content may bring to naught any negative impact of keyword cannibalization.
![]() By:Volha Belakurskaya
By:Volha Belakurskaya